Snoring in Children
Why is Your Child Snoring?
Children who struggle to breathe while snoring may be suffering from Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Hypoventilation Syndrome (OSAHS). These children may snort or gasp as they snore, and may appear to “suck in the chest”. OSAHS is described as breathing that starts and stops during sleep. The stoppage is usually caused when the throat narrows or even closes during sleep.
How do I Know if My Child’s Snoring is Serious?
- Sleep in an unusual position with head off the bed, propped up with many pillows or sleep sitting up
- Snore loudly and often
- Sleep restlessly
- Stop breathing during the night for a short period followed by snorting, gasping or completely waking up
- Sweat heavily during sleep
- Find difficulty in waking up, even though it seems he or she has had enough sleep
- Have headaches during the day, particularly in the morning
- Be irritable, aggressive or simply “cranky”
- Have school or other behavioural problems
- Fall asleep or daydream in school or at home
Some of these symptoms are similar to those described in children with Attention Deficit Hyperacitivity Disorder (ADHD), such as trouble concentrating, hyperactivity and nervousness. If you have noticed that your child has some of the above symptoms, you should talk to your paediatrician about referral to a sleep specialist.
What Actually Happens when My Child has Sleep Apnoea?
Your child’s muscles are more relaxed during sleep than they are during waking hours, including the muscles used in breathing. In some children with OSAHS, the throat muscles relax too much and interfere with breathing. In other children, the muscles relax normally during sleep, but a narrower than normal throat passage allows the throat to close. In these cases, when the child tries to breathe, he experiences something like trying to slurp a drink through a floppy, wet paper straw. You will hear deep gasps as your child’s breathing starts, and each gasp may awaken the child momentarily.
How do I Confirm if My Child has OSAHS?
You should consult your child’s paediatrician to determine if your child has OSAHS. The paediatrician may then refer him/her to a sleep specialist, if there is a suspicion of OSAHS. The sleep specialist will record your child’s sleep for at least one night in a laboratory with a test called polysomnography (PSG). This is the only way to find out if your child has OSAHS or has primary snoring. During the night, various small recording devices are placed on the child’s head and body to monitor the sleep pattern. They will also record the brain waves, leg and arm movements, muscle activity, heartbeat, and breathing pattern. These monitors do not pose any danger to the child, are not painful and are designed to be as comfortable as possible. The sleep study also allows the sleep specialist to determine how serious the OSAHS is, look for any associated sleep problems and to decide on the best treatment.
What are the Treatment Options for OSAHS?
Surgery
In many children, enlarged tonsils and adenoids are the cause of OSAHS and your doctor will recommend removing them. The procedure is called adenotonsillectomy. Other types of surgery, such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (when the uvula, tonsils and part of the soft palate are removed) and various types of jaw and facial surgery may be recommended if your child has a structural problem which is causing the OSAHS. Tracheostomy (opening a hole in the windpipe at the neck) is generally used only in life threatening OSAHS with no other suitable treatment available. Sometimes surgery can stop snoring even though it does not cure OSAHS. A second sleep study may be needed to be sure OSAHS has been cured. Follow the advice of your sleep specialist.
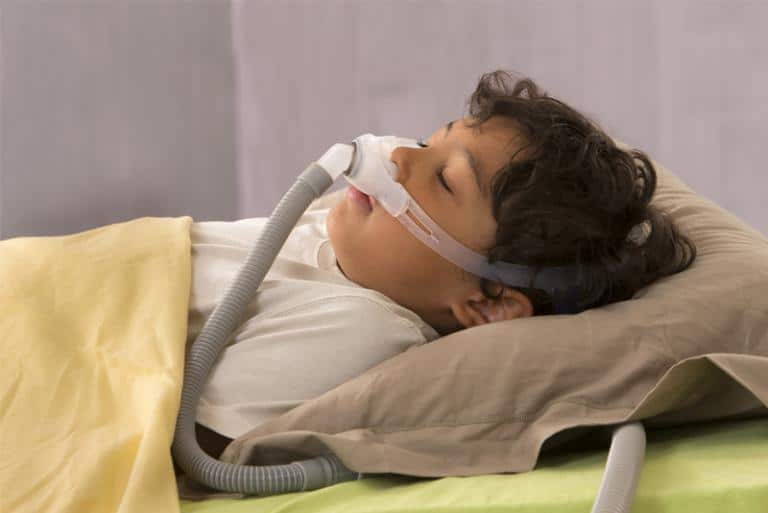
Positive Airway Pressure (PAP)
PAP is a small mask worn over the nose during sleep. The mask provides air pressure that keeps the throat from closing during sleep. PAP may be used to prepare the child before surgery and is also helpful for children when surgical treatment is not possible or desirable, or when surgery does not cure the OSAHS.
Weight Loss
If your sleep specialist thinks that obesity may be contributing to your child’s OSAHS, he may recommend weight loss by means of a combined diet, exercise and behavioural program. Even if other treatments are used, weight loss in the obese child with OSAHS helps to control OSAHS and sometimes lead to a cure.

